Getting Started
Let's discover EasyCarve in less than 5 minutes.
What is EasyCarve?
EasyCarve is a web-based CNC application that creates cutting instructions for your machine using 3D models from the Design & Make library.
To use EasyCarve successfully, you'll need:
- Access to a CNC router or milling machine
- Basic familiarity with your machine's operation
- Material to cut (wood, plastic, etc.)
- Cutting tools (end mills, ball nose bits, etc.) appropriate for your material
- Knowledge of your machine's capabilities and limitations
The EasyCarve Workflow
EasyCarve follows a simple process:
- Create Project - Choose a 3D model to carve
- Size & Position - Set dimensions and position within your material
- Select Machine - Tell EasyCarve which CNC machine you're using
- Set Up Tools - Define the cutting tools you have available
- Create Toolpaths - Generate cutting instructions (roughing, finishing, cutout)
- Export - Save files to run on your machine
- Toolpath: Step-by-step cutting instructions for your CNC machine. You might know these as G-code but lots of machines use different formats.
- Feeds and Speeds: How fast your machine moves and spins the cutting tool
- Material Origin: The starting point (X=0, Y=0, Z=0) where your machine begins cutting
- Post-processor: Translator that converts toolpaths into your specific machine's language
To start making a new model in EasyCarve begin by clicking the New Project button on the home page.
Create Your Project
Choose Your Model Type
Pick between Background models and Individual models:
- Background models come with pre-defined regions for attractive layouts
- Individual models can be used by themselves or within background regions
Think of backgrounds as templates or frames, while individual models are the decorative elements you want to carve. Background models provide structured layouts that are ready for machining, while individual models give you complete creative freedom.
Use either the right-hand controls to filter the models or use the search box to find specific models from D&M.

Import Background
If you start from a background, you can click any of the models to import them.
Import Model
If you start from an individual model, you can click any of the models, you will see that each EasyCarve model comes in 3 styles:
- Regular - Standard raised carving
- Dish - Carved into a recessed dish shape
- Recess - Carved as a pocket or inlay
Choose the style you like the most and click 'Import' to create your project.

Understanding the EasyCarve Interface
EasyCarve is structured into main parts:
- Project bar at the top with the name and controls
- Steps navigation to move between workflow steps
- Forms for entering data for each step
- The 3D View showing your project state
Layout
The Layout Step is where you arrange your design components:
- Add components to your design like backgrounds, models or text
- Modify existing components by clicking them
Text Edit
You can add text to your design by clicking the Add button and selecting 'Text'.
Enter the text you want to display and adjust its size and position.
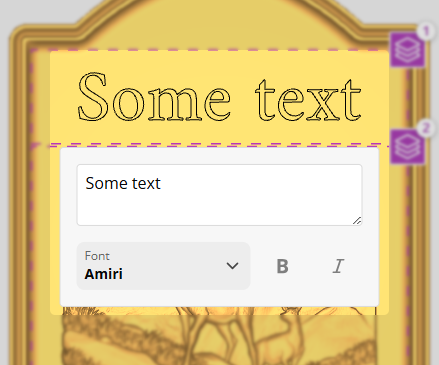
You can control different aspects of the text layout:
- Font: Choose a font
- Style: Choose a style (Bold / Italic)
- Font height: Scale your text up or down with the region's constraints.
- Line Spacing: Control the spacing between lines for box text
- Alignment: Horizontal/Vertical alignment within the text box or curve
Size & Position
The Size/Position Step makes your design fit your real-world setup:
- Set the final size of your carved model
- Choose your material type and thickness
- Position the model within your material
- Set where your machine starts cutting (origin point)
Units
In every part of this step, you can adjust the units of your project using the Project units toggle.
Model

We begin by setting the size of the model. If you change one dimension, then the other dimension is fixed. If you wish to make the model thicker or thinner without changing the width and height then you can use the link button to unlink the dimensions.
The Orientation section allows you to rotate and mirror the design. We can adjust the orientation of the model to rotate it 90 degrees by clicking the 'Rotate' button. We can also choose to mirror the model. This is done by clicking the 'Mirror' button.


Material Setup
In the material step:
- Material type:
Choose your material (pine, oak, MDF, etc.) or
add a new one
-
Material Thickness
: Enter your stock material thickness - Model position: Choose where the model sits within the material
The material needs to be thick enough to accommodate your design. If not, you can go back to adjust your model depth. If your design isn't as thick as the material, you can position it towards the top (with a thick base) or towards the bottom (with no base).


Material Origin
In the material origin step, set where your machine starts cutting (X=0, Y=0, Z=0).
This tells your machine where to begin cutting and is crucial for positioning your material correctly on the machine bed. Think of this as choosing which corner or edge of your material the machine should use as its reference point.

Select Machine
In the machine selection step, choose your CNC machine. If this is your first time, 'Add new machine' from our presets.
EasyCarve needs to know which CNC machine you're using because different machines have different capabilities, sizes, and require different file formats (post-processors). This ensures the generated toolpaths will work correctly with your specific machine.
To learn more about machines, see the Tool Database guide.

Set Up Your Tools
Tell EasyCarve what cutting tools you have available in your Tool Database.
To access: settings menu → 'Manage tools'
Different tools cut differently - a small end mill removes material slowly but gives fine detail, while a large end mill removes material quickly but can't do intricate work. EasyCarve needs to know:
- What size tools you have
- What type they are (end mill, ball nose, etc.)
- How fast they can safely cut your chosen material

Click 'Add Tool' and fill in the form to match your tool. Then set up feeds and speeds for your material and machine combination.

When prompted, you're telling EasyCarve how fast your tool can safely cut your material. You can set different speeds for different materials using the same tool - this means you don't need separate tool entries for each material type.

Create Toolpaths
Generate cutting instructions for your machine. Start with Toolpath Tabs (safety bridges), then create toolpaths.
Toolpath Tabs
Tabs are small bridges of material that keep your finished piece attached until you're ready to remove it safely. Auto-generate tabs with appropriate size and thickness.
Toolpath Types
Add toolpaths from the toolpath list:
| Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Roughing | Removes bulk material quickly |
| Finishing | Creates smooth final surface |
| VCarving | Creates a V-Carving toolpath for text |
| Cutout | Cuts piece free (optional) |
- Roughing: Always use first - like rough carpentry, removes most material
- Finishing: Use for detailed, smooth finish - usually with ball-nose tools
- V-Carving: Use for cutting text - usually with V-Bit tools
- Cutout: Only needed if you want to completely separate your carving from surrounding material
Most projects need roughing and finishing. Cutout is optional.
Creating Toolpaths
For each type: Click the toolpath section → Select tool → Set parameters → Click 'Calculate'
EasyCarve shows a preview of the cutting path. Use the view toggle for wireframe/simulation and job summary toggle for details.

- Roughing: Set machining allowance (material to leave for finishing) and cutting angle
- Finishing: Usually uses ball-nose tools for curved surfaces
- V-Carving: Usually uses v-carving tools for cutting the text
- Cutout: Set final pass height (leave material for hand finishing) and cut direction

Export
Convert your toolpaths into files your CNC machine can understand.
Go to the Export Step and see your job summary.
-
Select the appropriate post-processor
for your machine -
Select each toolpath
to export - Click export - files download automatically


- Post-processor: Translates toolpaths into G-code your machine understands
- Multiple toolpaths: Export separately to run one at a time, or together for automatic sequencing
- File transfer: Use USB, SD card, or network to get files to your machine
Next Steps
Transfer files to your CNC machine and you're ready to cut!
Always run a test cut on scrap material first, especially when trying new settings or materials!